This post was originally published on Medium
General aspects about sensors
Android devices tend to be accompanied with a series of sensors that make the device to interact with the environment that surrounds it.
And that’s already great to have a range of possibilities about what we can do in our applications,these sensors allow the terminal to have a knowledge of the environment that surrounds you,but the sensors are nothing more than electronic parts that capture information from outside and it is the application which should transform this information into data to work them.

The activities who works with sensors must implement the interface SensorEventListener that will force us to implement the methods onAccuracyChanged() y onSensorChanged() .
The method onAccuracyChanged() will be executed when the precision of a sensor change , while onSensorChanged() will do it every time there is a change in one of the sensors.
Building an accelerometer app
The topic of sensors in android is tremendously big and it can’t be covered at all in one article, so for this occasion we will be build an accelerometer app, metallball 💥.

But first a little bit about this sensor in specific.
Accelerometer
With this kind of sensor it’s possible to determinate the orientation of the terminal in the real world 🌎 , considering as coordinate axis the middle point of the device.
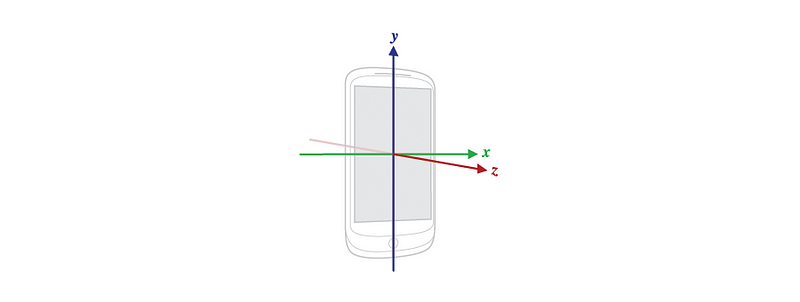
The accelerometer calculates the linear acceleration in each of the 3 axes (x, y, z); each axis has its own accelerometer, so that the data can be received individually.
The app code
In the MainActivity file you access to the vibration service, for that reason don’t forget to copy this into the AndroidManifest file.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.VIBRATE" />
Here is the full code of the app, If you have questions, post it to be able to answer.
package com.projects.enzoftware.metalball
import android.app.Service
import android.bluetooth.BluetoothClass
import android.content.Context
import android.content.pm.ActivityInfo
import android.graphics.Bitmap
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory
import android.graphics.Canvas
import android.graphics.Point
import android.hardware.Sensor
import android.hardware.SensorEvent
import android.hardware.SensorEventListener
import android.hardware.SensorManager
import android.os.Build
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.os.Vibrator
import android.view.*
class MetalBall : AppCompatActivity() , SensorEventListener {
private var mSensorManager : SensorManager ?= null
private var mAccelerometer : Sensor ?= null
var ground : GroundView ?= null
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// get reference of the service
mSensorManager = getSystemService(Context.SENSOR_SERVICE) as SensorManager
// focus in accelerometer
mAccelerometer = mSensorManager!!.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER)
// setup the window
requestedOrientation = ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE
window.setFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN)
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB){
window.decorView.systemUiVisibility = View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_STABLE
View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_HIDE_NAVIGATION
View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_FULLSCREEN
View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_HIDE_NAVIGATION
View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_FULLSCREEN
View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_IMMERSIVE
}
// set the view
ground = GroundView(this)
setContentView(ground)
}
override fun onAccuracyChanged(sensor: Sensor?, accuracy: Int) {
}
override fun onSensorChanged(event: SensorEvent?) {
if (event != null) {
ground!!.updateMe(event.values[1] , event.values[0])
}
}
override fun onResume() {
super.onResume()
mSensorManager!!.registerListener(this,mAccelerometer,
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_GAME)
}
override fun onPause() {
super.onPause()
mSensorManager!!.unregisterListener(this)
}
class DrawThread (surfaceHolder: SurfaceHolder , panel : GroundView) : Thread() {
private var surfaceHolder :SurfaceHolder ?= null
private var panel : GroundView ?= null
private var run = false
init {
this.surfaceHolder = surfaceHolder
this.panel = panel
}
fun setRunning(run : Boolean){
this.run = run
}
override fun run() {
var c: Canvas ?= null
while (run){
c = null
try {
c = surfaceHolder!!.lockCanvas(null)
synchronized(surfaceHolder!!){
panel!!.draw(c)
}
}finally {
if (c!= null){
surfaceHolder!!.unlockCanvasAndPost(c)
}
}
}
}
}
}
class GroundView(context: Context?) : SurfaceView(context), SurfaceHolder.Callback{
// ball coordinates
var cx : Float = 10.toFloat()
var cy : Float = 10.toFloat()
// last position increment
var lastGx : Float = 0.toFloat()
var lastGy : Float = 0.toFloat()
// graphic size of the ball
var picHeight: Int = 0
var picWidth : Int = 0
var icon:Bitmap ?= null
// window size
var Windowwidth : Int = 0
var Windowheight : Int = 0
// is touching the edge ?
var noBorderX = false
var noBorderY = false
var vibratorService : Vibrator ?= null
var thread : MetalBall.DrawThread?= null
init {
holder.addCallback(this)
//create a thread
thread = MetalBall.DrawThread(holder, this)
// get references and sizes of the objects
val display: Display = (getContext().getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE) as WindowManager).defaultDisplay
val size:Point = Point()
display.getSize(size)
Windowwidth = size.x
Windowheight = size.y
icon = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(resources,R.drawable.ball)
picHeight = icon!!.height
picWidth = icon!!.width
vibratorService = (getContext().getSystemService(Service.VIBRATOR_SERVICE)) as Vibrator
}
override fun surfaceChanged(holder: SurfaceHolder?, format: Int, width: Int, height: Int) {
}
override fun surfaceDestroyed(holder: SurfaceHolder?) {
}
override fun surfaceCreated(holder: SurfaceHolder?) {
thread!!.setRunning(true)
thread!!.start()
}
override fun draw(canvas: Canvas?) {
super.draw(canvas)
if (canvas != null){
canvas.drawColor(0xFFAAAAA)
canvas.drawBitmap(icon,cx,cy,null)
}
}
override public fun onDraw(canvas: Canvas?) {
if (canvas != null){
canvas.drawColor(0xFFAAAAA)
canvas.drawBitmap(icon,cx,cy,null)
}
}
fun updateMe(inx : Float , iny : Float){
lastGx += inx
lastGy += iny
cx += lastGx
cy += lastGy
if(cx > (Windowwidth - picWidth)){
cx = (Windowwidth - picWidth).toFloat()
lastGx = 0F
if (noBorderX){
vibratorService!!.vibrate(100)
noBorderX = false
}
}
else if(cx < (0)){
cx = 0F
lastGx = 0F
if(noBorderX){
vibratorService!!.vibrate(100)
noBorderX = false
}
}
else{ noBorderX = true }
if (cy > (Windowheight - picHeight)){
cy = (Windowheight - picHeight).toFloat()
lastGy = 0F
if (noBorderY){
vibratorService!!.vibrate(100)
noBorderY = false
}
}
else if(cy < (0)){
cy = 0F
lastGy = 0F
if (noBorderY){
vibratorService!!.vibrate(100)
noBorderY= false
}
}
else{ noBorderY = true }
invalidate()
}
}
Conclusion
If you found this helpful, click the ![]() below. Follow me for more articles on technology.
below. Follow me for more articles on technology.
Here is the link to the full source code 💥